上海交通大学区域光纤通信网与新型光通信系统国家重点实验室,上海 200240
提出一种将质子交换技术和刻蚀技术结合的体铌酸锂波导和器件加工方案,基于质子交换的铌酸锂晶体相变特性改变,降低了质子交换区直接刻蚀难度,结合质子交换的纵向折射率改变和刻蚀波导的横向结构改变,波导尺寸显著降低,采用粒子群算法优化波导尺寸,最小可达2.5m。基于该工艺方案设计了中心波长为1550 nm、四通道且通道间隔为400 GHz的阵列波导光栅,该阵列波导光栅的传输损耗约为6 dB,相邻通道间串扰均低于22 dB,整体尺寸仅为850 ×620 μm,在高密度铌酸锂光子集成互连等场景具有较大的应用潜力。
光栅 铌酸锂 质子交换 粗波分复用 阵列波导光栅 光学学报
2023, 43(13): 1305003
1 湖北工业大学机械工程学院,湖北 武汉 430068
2 湖北省现代制造质量工程重点实验室,湖北 武汉 430068
为确定线结构光视觉传感器与工业机器人法兰中心的位姿关系,设计了一种只有单个圆的平面靶标及标定方法。调整机器人姿态,使激光线经过平面靶标上实心圆的圆心,通过图像处理,得到圆心的像素坐标,转换后得到圆心在传感器坐标系下的坐标;多次调整姿态,获取多组图像,得到多组传感器坐标系下圆心坐标;结合对应机器人位姿关系,采用最小二乘法直接解算出手眼矩阵。实验结果表明,所提方法与采用标准球为靶标的手眼标定方法对比,反求得到的三维坐标的标准差由0.3893 mm降为0.2145 mm,以同一目标的不同间距为测量对象,均方根误差均有效减小。该方法提高了标定精度,不需要采用昂贵的靶标,适合于现场标定。
机器视觉 线激光 平面靶标 手眼标定 机器人标定 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(10): 1015002
1 广东海洋大学智慧海洋传感网及其装备工程技术研究中心, 广东 湛江 524088
2 哈尔滨理工大学测控技术与通信工程学院, 黑龙江 哈尔滨 150080
提出并制备了一种基于聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)膜封装空芯光纤的级联双腔温度传感器。该传感器由空气腔(FP1)和PDMS腔(FP2)级联而成,且PDMS腔长度远小于空气腔长度,从而使该传感器满足游标效应产生条件[FP1腔与复合腔FP3(由FP1和FP2组成)的光程接近]。当外界温度变化时,PDMS膜向两侧膨胀,导致FP1腔和FP3腔的干涉谱向相反的方向移动。实验结果表明,FP1腔和FP3腔干涉谱产生了游标效应,干涉谱包络明显;在50~60 ℃范围内,温度灵敏度达到1.32 nm/℃,该结果与理论分析结果相符。该传感器具有体积小、结构轻、灵敏度高、制备简单等优点,在化学、生物、医疗等领域具有潜在的应用价值。
光纤传感器 游标效应 法布里-珀罗干涉仪 高灵敏温度检测

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
2 Peng Cheng Laboratory, Shenzhen 518055, China
Optical signaling without a high voltage driver for electric-optic modulation is in high demand to reduce power consumption, packaging complexity, and cost. In this work, we propose and experimentally demonstrate a silicon mode-loop Mach–Zehnder modulator (ML-MZM) with record-high modulation efficiency. We used a mode-loop structure to recycle light twice in the phase shifter. With an L-shaped PN junction, a comparably large overlap between the PN junction and optical modes of both and was achieved to lower the driving voltage or decrease the photonic device size. Proof-of-concept high-efficiency modulation with low of was obtained. Subvoltage can be realized with a millimeter’s length phase shifter by this scheme, which makes the realization of CMOS-compatible driverless modulation highly possible. 40 Gb/s signaling with a bit error rate below the 7% forward-error-correction threshold was then demonstrated with the fabricated ML-MZM, indicating great potential for high-speed optical communication.
Photonics Research
2022, 10(1): 01000214
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
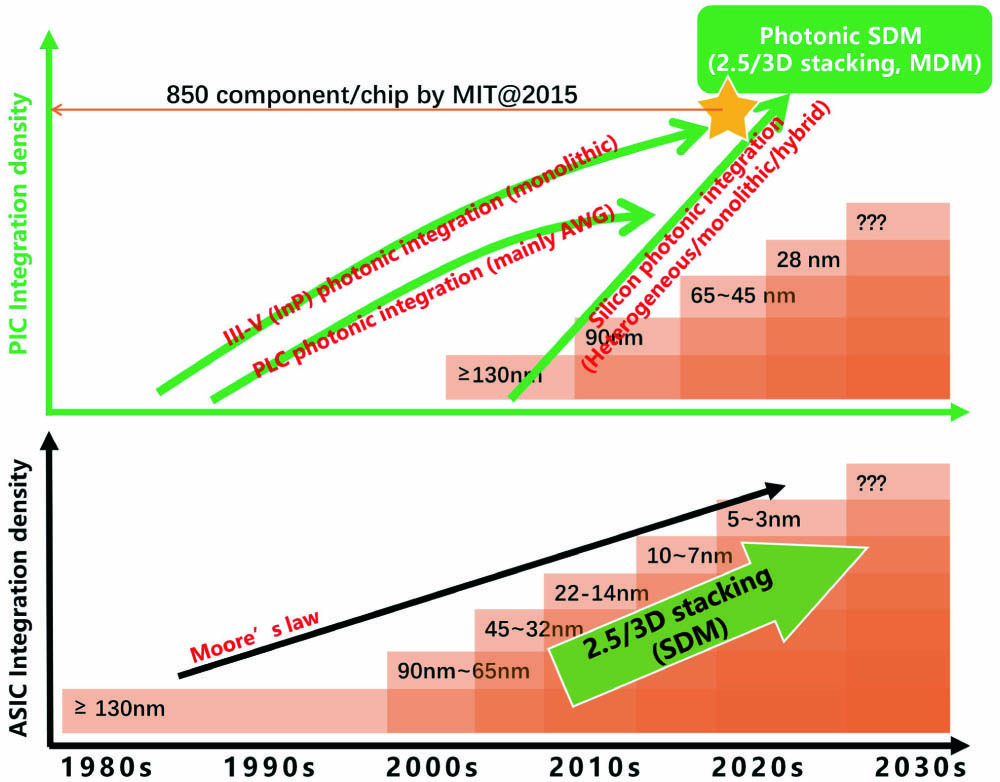
To overcome the capacity crunch of optical communications based on the traditional single-mode fiber (SMF), different modes in a few-mode fiber (FMF) can be employed for mode division multiplexing (MDM). MDM can also be extended to photonic integration for obtaining improved density and efficiency, as well as interconnection capacity. Therefore, MDM becomes the most promising method for maintaining the trend of “Moore’s law” in photonic integration and optical fiber transmission. In this tutorial, we provide a review of MDM works and cutting-edge progresses from photonic integration to optical fiber transmission, including our recent works of MDM low-noise amplification, FMF fiber design, MDM Si photonic devices, and so on. Research and application challenges of MDM for optical communications regarding long-haul transmission and short reach interconnection are discussed as well. The content is expected to be of important value for both academic researchers and industrial engineers during the development of next-generation optical communication systems, from photonic chips to fiber links.
mode division multiplexing photonic integration few-mode fiber optical transmission optical interconnection Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(9): 091301
Author Affiliations
Abstract
State Key Laboratory of Advanced Optical Communication Systems and Networks, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai 200240, China
We report a low-fabrication-complexity and wideband fiber lens, which is formed by fiber facet etching and filling high refractive index UV adhesive. The optical field can be significantly shrunk by the facet lens so as to obtain improved optical coupling. Numerical simulations were carried out for different coupling conditions, on both fundamental mode and high-order mode, for a nine-mode fiber. The fundamental mode area can be reduced from 152.17 to , and the coupling loss between the fiber lens and a photonic waveguide can be reduced to with over 1000 nm 3 dB bandwidth.
fiber lens optical coupling Chinese Optics Letters
2021, 19(5): 050602
1 华南理工大学发光材料与器件国家重点实验室
2 华南理工大学材料科学与工程学院, 广州 510640
3 惠州雷士光电科技有限公司, 广东 惠州 516021
采用模压成型和真空压力浸渗工艺制备了高体积分数SiC增强Al基复合材料(AlSiC)。物相和显微结构研究结果表明, 此种方法制备的AlSiC复合材料, 组织致密且大小两种粒径的SiC颗粒均匀分布于Al基质中, 界面结合强度高;SiC增强颗粒与Al基质界面反应控制良好, 未出现Al4C3脆性相。对Al4C3相形成机理进行了分析, 指出6061铝合金中的Si元素和真空压力浸渗工艺条件有利于防止脆性相Al4C3的形成。热性能测试结果表明, 随温度升高, 复合材料热膨胀系数先增大后减小, 315℃附近出现最大值。所获得复合材料的平均热膨胀系数为7.00×10-6℃-1, 热导率为155.1W/mK, 密度为3.1g/cm3, 完全满足高性能电子封装材料的要求。
显微结构 物相 热膨胀系数 AlSiC AlSiC microstructure phase coefficient of thermal expansion
1 华南理工大学发光材料与器件国家重点实验室
2 华南理工大学材料科学与工程学院,广州 510640
3 华南理工大学惠州雷士光电科技有限公司,广东 惠州 516021
采用模压成型和真空压力浸渗工艺制备了高体积分数SiC增强Al基复合材料(AlSiC)。物相和显微结构研究结果表明,此种方法制备的AlSiC复合材料,组织致密且大小两种粒径的SiC颗粒均匀分布于Al基质中,界面结合强度高; SiC增强颗粒与Al基质界面反应控制良好,未出现Al4C3等脆性相。在此基础上,研究了基体金属、粘结剂用量、粗细SiC颗粒比例对复合材料热导率的影响。结果表明,以1A90高纯铝为基体的复合材料的热导率高于以6061铝合金为基体的复合材料的热导率; 粘结剂用量减少时,复合材料热导率提高; 当SiC体积分数一定时,AlSiC复合材料的热导率随增强体中粗颗粒SiC比例增大而增大。
热导率 基体 粘结剂 AlSiC AlSiC thermal conductivity matrix binder SiC SiC





